If you want to know about bad links pointing to your website and Tips for Spotting and Fixing Them on Your Site we have you covered.
Backlinks are two of the most crucial ranking factors that can help your website increase its search positions for your target keywords.
So, it follows that the more backlinks you build, the higher chances you can rank on top of search engine results pages (SERPs), right?
Wrong!
It’s not the quantity that’s important. Instead, the quality of links you build for your website is vital in helping it rank at the top of Google organic search.
That said, not all links will help improve your site’s organic rankings—some of them can even drag your website down in search results!
To prevent this from happening, you must learn everything about bad links: the characteristics of low-quality links, the types of backlinks search engines don’t like, and what to do if your site has spammy links.
Knowing these things discussed in this post will help you build better links moving forward and protect your website from spammy link building.
What Makes a Backlink “Bad?”
For starters, let’s revisit how backlinks work: as akin to a recommendation.
A high-authority website linking to your site works the same way as an influencer or a figurehead in your industry recommending their audience to your work or services.
Suddenly, you’ll receive more inquiries about your services and generate more revenue from new clients.
Let’s say an infamous person or someone whom you don’t want to associate yourself with praises your work to people. Their “glowing recommendations” can serve as a black mark in the eyes of your audience or people in the industry.
The same thing applies to link building.
A backlink from an undesirable website can do more harm to your site than good.
If you have lots of these bad links pointing to your site, Google will associate your site with an undesirable website, which could hurt your rankings.
Now, this is where Google steps in to determine which links are not good.
Google sees this type of backlinks as part of a link scheme with the intent of gamifying the search engine’s algorithm.
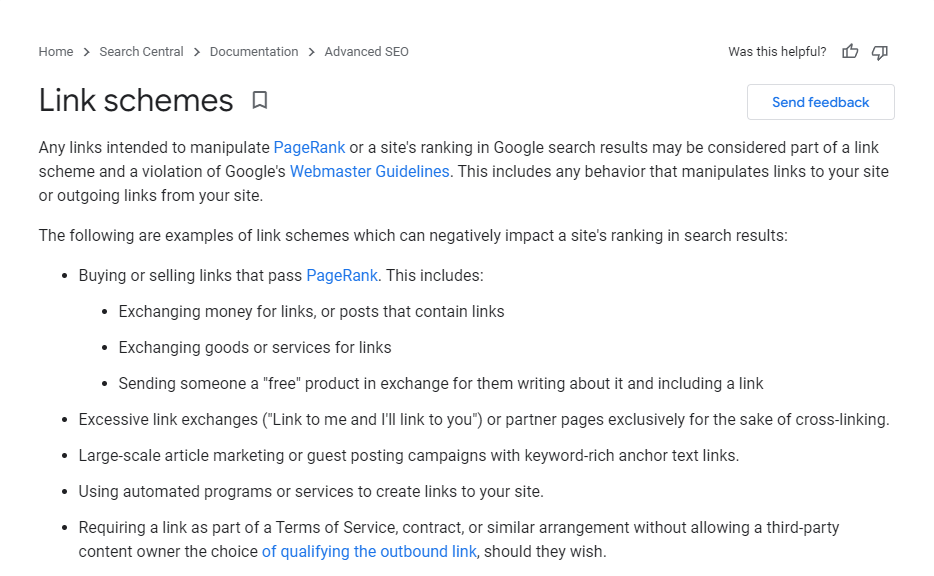
There are many cases in which the links are so good that they can overpower their way to the top of search results despite poor on-page factors.
But since they’re created to manipulate search algorithms, Google penalizes a site with these backlinks by disregarding these links in ranking the website. As a result, the site will drop on SERPs and may not be able to rank on top again!
Whether you agree with Google’s definition of a link scheme or not, one thing is clear:
Backlinks are considered “bad” if they don’t add value to, if not damage, your website.
In particular, a bad link comes from sites that share common characteristics with spammy websites.
Below is a short list of qualities that these spammy sites have in common:
- Thin content.
- Loads very slowly.
- Generic web design.
- Lots of ads.
- Lots of outbound links.
- No social media presence.
Essentially, these sites are designed to look natural—at least in the eyes of Google. But they are manufactured to initially help but ultimately hurt websites that have a link from them.
Therefore, your goal is to determine how your site got bad backlinks and the kind of sites they were built on.
Later, you’ll find out that not all bad links are self-inflicted—some are created behind your backs and will hit you unsuspectedly upon an algorithm update.
Types of Bad Backlinks
Now that we’re on the same page regarding bad backlinks, let’s look at how this backlink type is created.
There are lots of bad backlinks out there, such as spammy blog comment links, forum links, and backlinks from low-quality directories, to name a few. But none of these are as damaging as the ones listed below:
Guest Post Links from a Public Listing
You might have received emails such as this one:
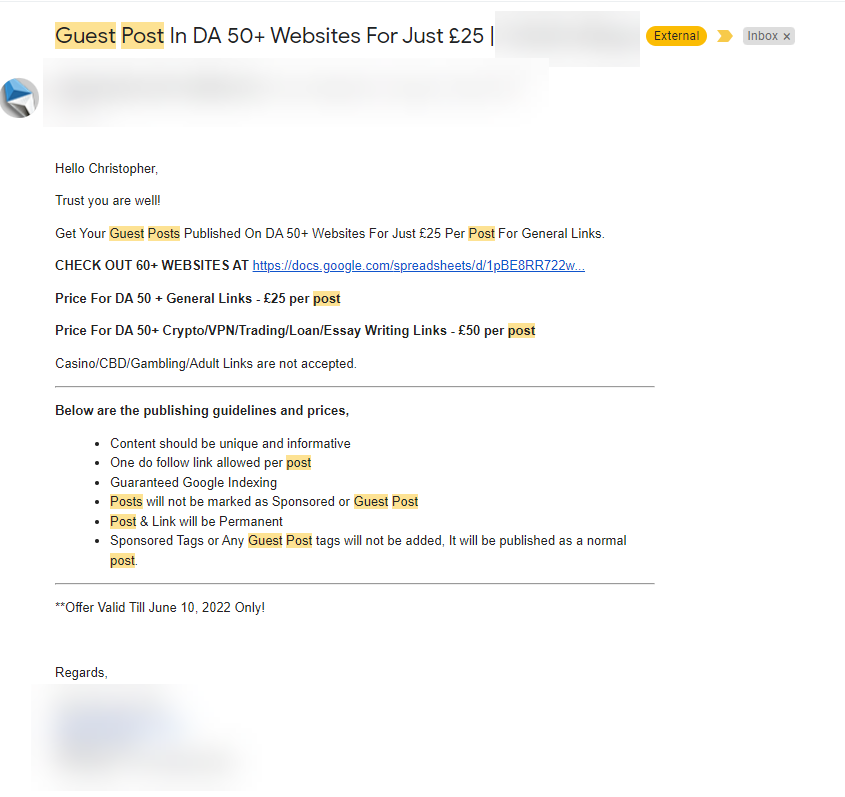
It’s an offer to include your links in a guest post to be published on a site with a Domain Authority (DA) of at least 50, which is pretty authoritative.
In the email, there’s also a Gdocs link to the list of sites with at least DA 60.
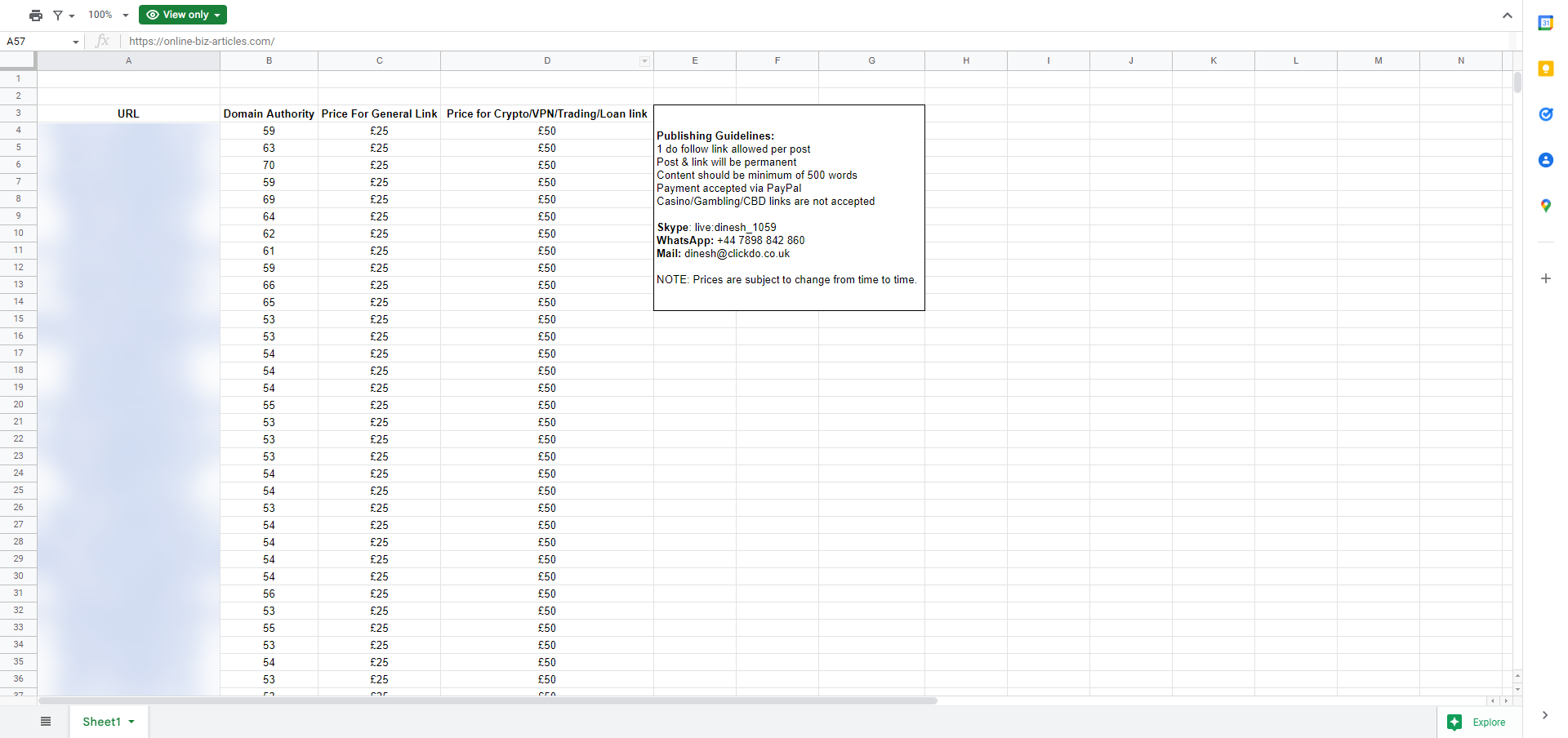
To be clear, there’s nothing wrong with building links via guest posting, especially when done correctly. Getting a blog post published on another site with a backlink to your website is a great way to build your link profile.
Also, link buying is common in the industry—it’s just a matter of making your backlinks as natural and contextual as possible so that it adds value to the content.
However, the email broke an essential rule in effective link building:
You don’t buy backlinks on sites that search engines can trace back to their buyer.
Buying links from a list that is probably sent en masse could lead to your site’s demise, no matter how contextual or useful your link is in the blog post.
The fact that many people have the same list you receive could mean that somebody could have reported the sites to Google.
Worse, somebody from Google got hold of the list and blacklisted the sites from their algorithm.
Therefore, monitor your site’s SEO closely if you bought backlinks from vendors spreading their guest posting list to others.
It’s highly possible that nothing’s happened to your website yet, but you can’t be too sure based on how dynamic Google’s algorithm is.
Cheap Link Services
According to Murphy’s Law, if it’s too good to be true, it probably is.
While there are a few exceptions to the rules, finding cheap but effective link-building services is scarce.
Most of the time, the link they’ll build for your site will bite you back in the long run, especially after a Google algorithm update.
Sites like Fiverr with people offering $5 for DA 90+ links are those you should avoid as much as possible.
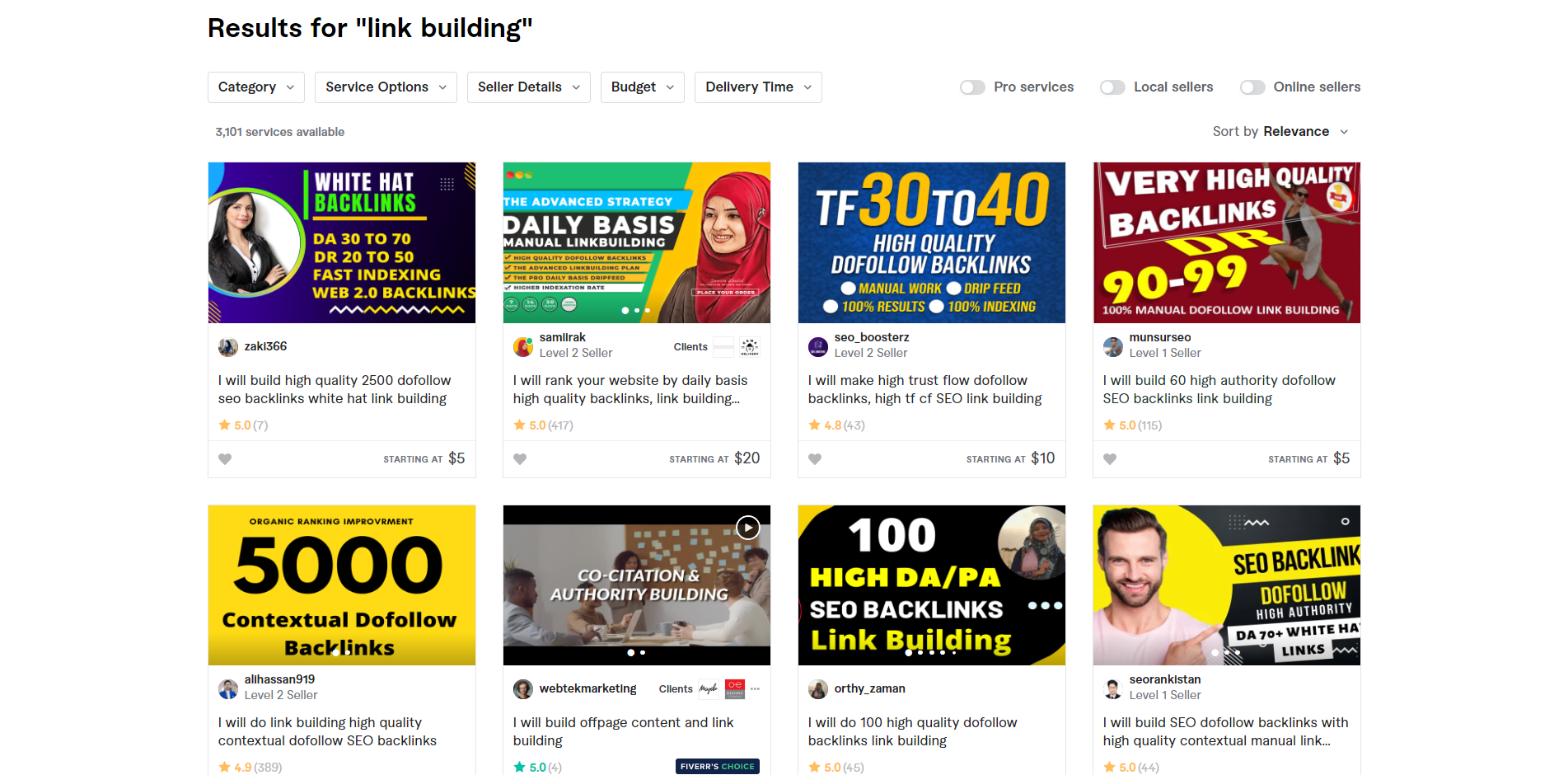
To be fair, not everybody on these platforms is untrustworthy. So if you’re feeling frisky, you could buy a few links on your test sites and see how the backlinks help the website perform over time.
However, it’s just better to get with tried and true tactics from vendors with years of experience under the belt, despite being more expensive.
(Poorly Constructed) PBNs
PBNs, also known as private blog networks, refer to a group of blogs used to build links to client and money sites.
Blogs in this network usually have high SEO metrics such as DA, DR (Ahrefs’ Domain Rating), and Flow Metrics (Majestic’s Trust Flow and Citation Flow).
Using their authority, site owners can get backlinks from them to boost their search rankings faster than any other link building strategy.
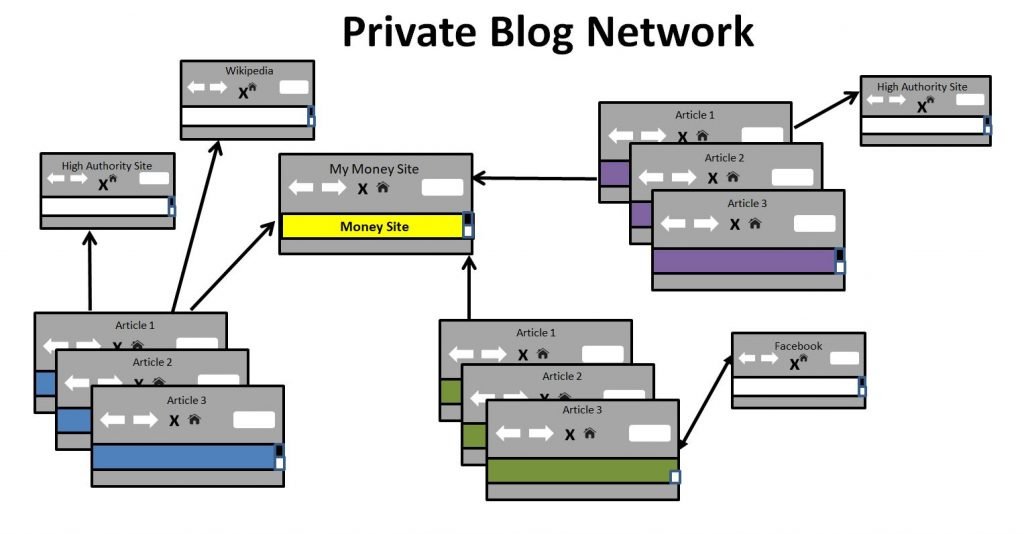
So, why is this considered a bad backlink, then?
There’s just so much riding on PBN links that you risk your site from getting exposed and penalized in the process.
For example, linking from the homepages of PBNs to your money page is a big no-no.
In theory, linking straight from any homepage to the money site is always better to maximize the link juice.
But if you do this often, Google could uncover your link building pattern, allowing them to trace back to the sites.
From here, the search engine can see similarities among these sites, such as blog layout, content structure, and others, to determine if they’re part of the same PBN. This results in penalization and the end of your website ranking on organic search.
How you link from PBNs is just one of the many precautions you have to worry about when using PBNs for link building. For instance, how you set up your blogs so Google can’t trace them back to you as their owner is another cause for concern.
That said, links coming from PBNs could still work ONLY IF PBN owners cover their tracks very well. And you can only know this if you have a close working relationship with the owner.
Other than just, you’re better off avoiding this technique like the plague if you don’t know what you’re doing.
Illegal Link Insertions
Link insertions or niche edits are another link building technique commonplace in the industry.
Instead of submitting a guest post to be published on another site, you can request the owner to include your dofollow links on an existing, indexed page on their site.
Since Google has already picked up this page and is already appearing on search results, the backlinks you can get from it are more powerful than a link from a new post.
These are perfectly legal in the eyes of Google as long as the links add value to the content.
However, it becomes bad when the links are inserted illegally.
A Buzzfeed recently article shed light on “hacked links.” It showed legitimate site owners who were surprised that their websites contained links they didn’t include in their pages.
The links were stealthily added to the site via an injected script that allows people to profit by including client links on these websites.
Illegal link insertions work both ways as well.
Aside from helping clients rank higher on SERPs, link insertions can also harm a website by receiving hacked backlinks from spammy websites.
The script was added to your site due to existing vulnerabilities in one’s CMS, like WordPress, or the lack of malware protection.
Similar to PBNs, you need to know if the vendor who sells links via insertions is to be trusted or not. Otherwise, you should look for other ways to build your backlink profile.
Negative SEO
This is not necessary a type of bad backlink. Instead, it’s a “strategy” that, instead of helping websites rank higher on SERPs with high-quality backlinks, does the same thing to achieve the opposite results.
Negative SEO, unfortunately, exists in the industry. By creating spammy backlinks on competitor sites, competitors can drag your site down their level, which allows them to outrank you in the process.
This is essentially putting the saying, “If I can’t win, then nobody can!” in the context of SEO.
Lots of negative SEO has been documented through the years. From Spencer Haws’ post in 2013 to Kinsta’s more recent documentation of their negative SEO experience, no one is safe from this kind of SEO attack.
If negative SEO significantly damages your site, there are ways to recover from it. But the process requires lots of work that you shouldn’t be doing in the first place.
Tools to Use for Spotting Bad Backlinks
As mentioned, bad links are from sites that share similarities with spammy websites.
Usually, you want to check each site and see if it passes the eye test as genuine. However, reviewing each one manually is a time-consuming process.
In this case, you’re better off using a tool that enables you to extract all your backlinks.
Below are some of the best ones available:
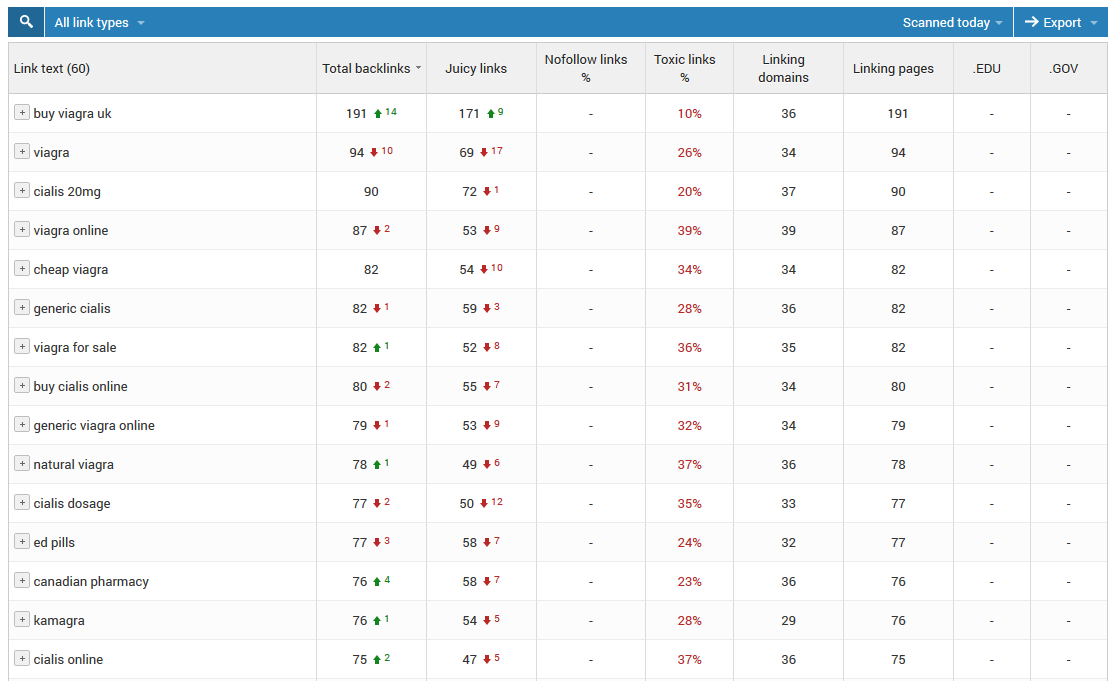
SEMrush
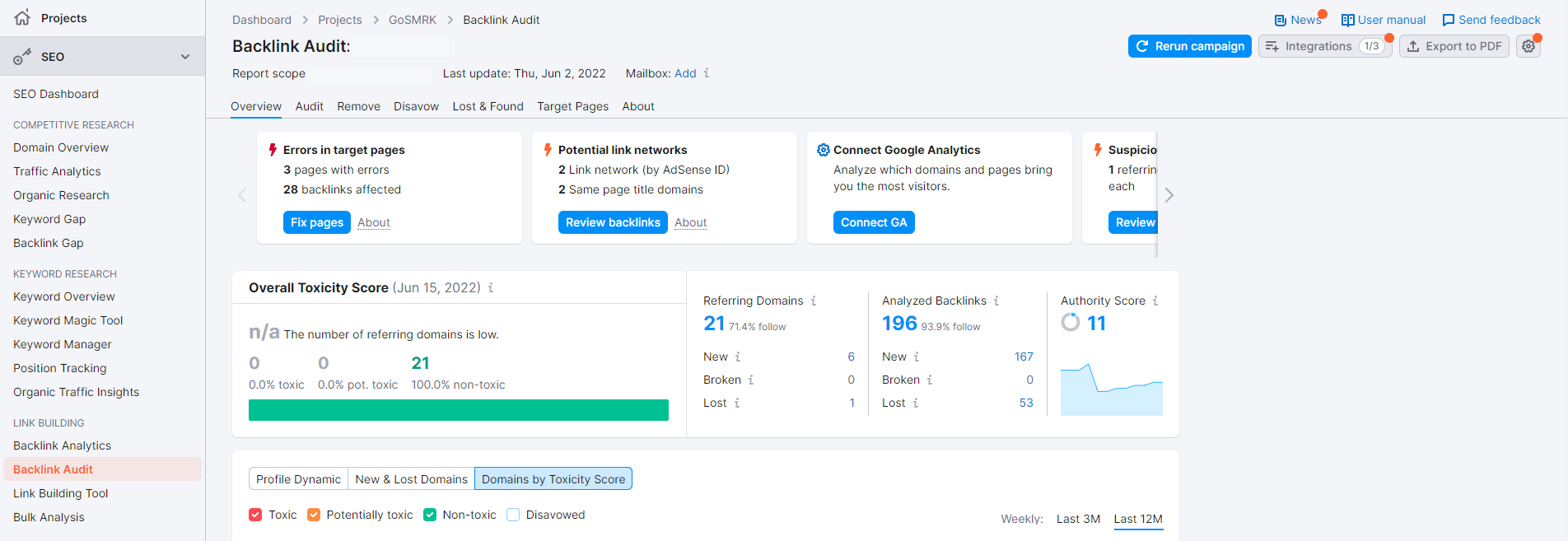
SEMrush‘s Backlink Audit tool is perfect for this purpose.
From your SEMrush dashboard, click on Link Building > Backlink Audit on the sidebar. Then enter your domain URL on the search bar so the tool can analyze your site’s backlinks.
On the next page, SEMrush determines which among your links are toxic and are most likely preventing your website from ranking higher on SERPs.
Link Research Tools
Another option is Link Research Tools, which is arguably a more robust link analysis tool thanks to its World famous Link Detox® and Link Detox Boost®.
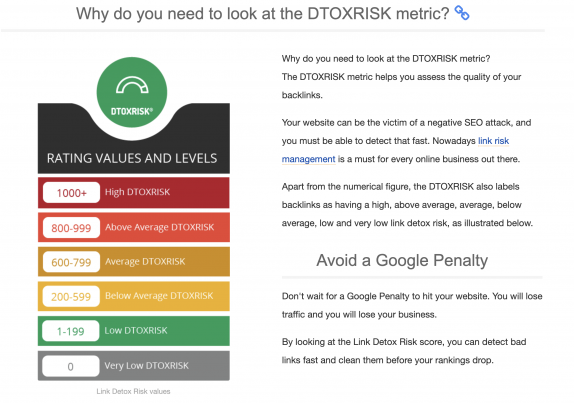
Both features provide you with a more extensive view of your link profile, in which each link is broken down into different SEO metrics.
They provide you with all the information you need to help develop an SEO campaign to combat negative SEO and build a better link building campaign.
On the downside, LRT is one of the more expensive ones on the market. It’s a recommended tool if you have a large site and are constantly bombarded with spammy links by competitors.
Monitor Backlinks
If you’re looking for a cheaper alternative to SEMrush and LRT, Monitor Backlinks is your tool.
Run a backlink audit and cross-reference the referring domains across popular SEO variables.
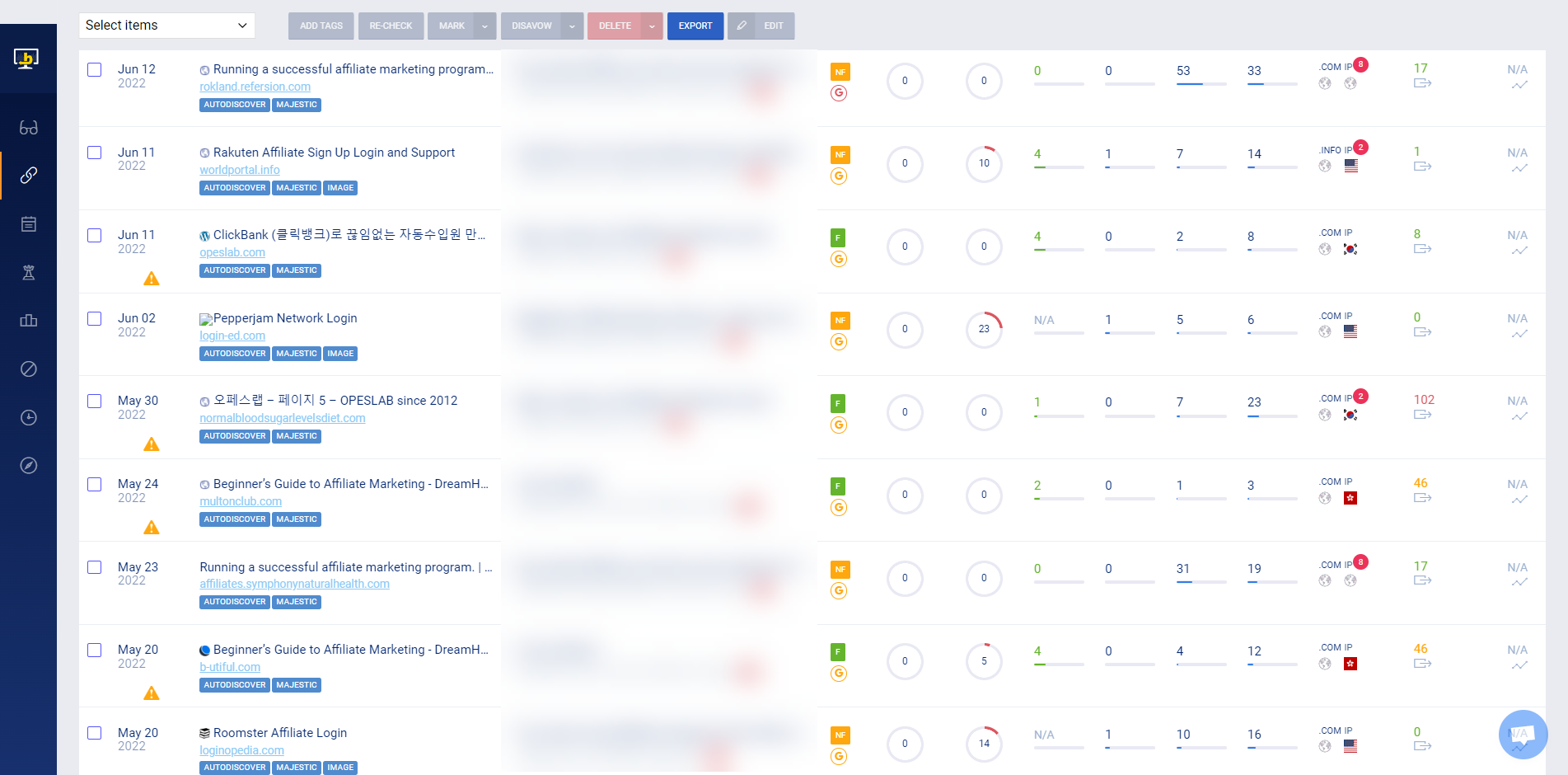
You can also run a link analysis to check your backlinks according to factors like TLD, IP location, anchor text, dofollow vs. nofollow links, and others.
Backlink Blacklist
Finally, if you’re working on a limited budget, you can run a quick search on Backlink Blacklistof the referring domains in your link profile.
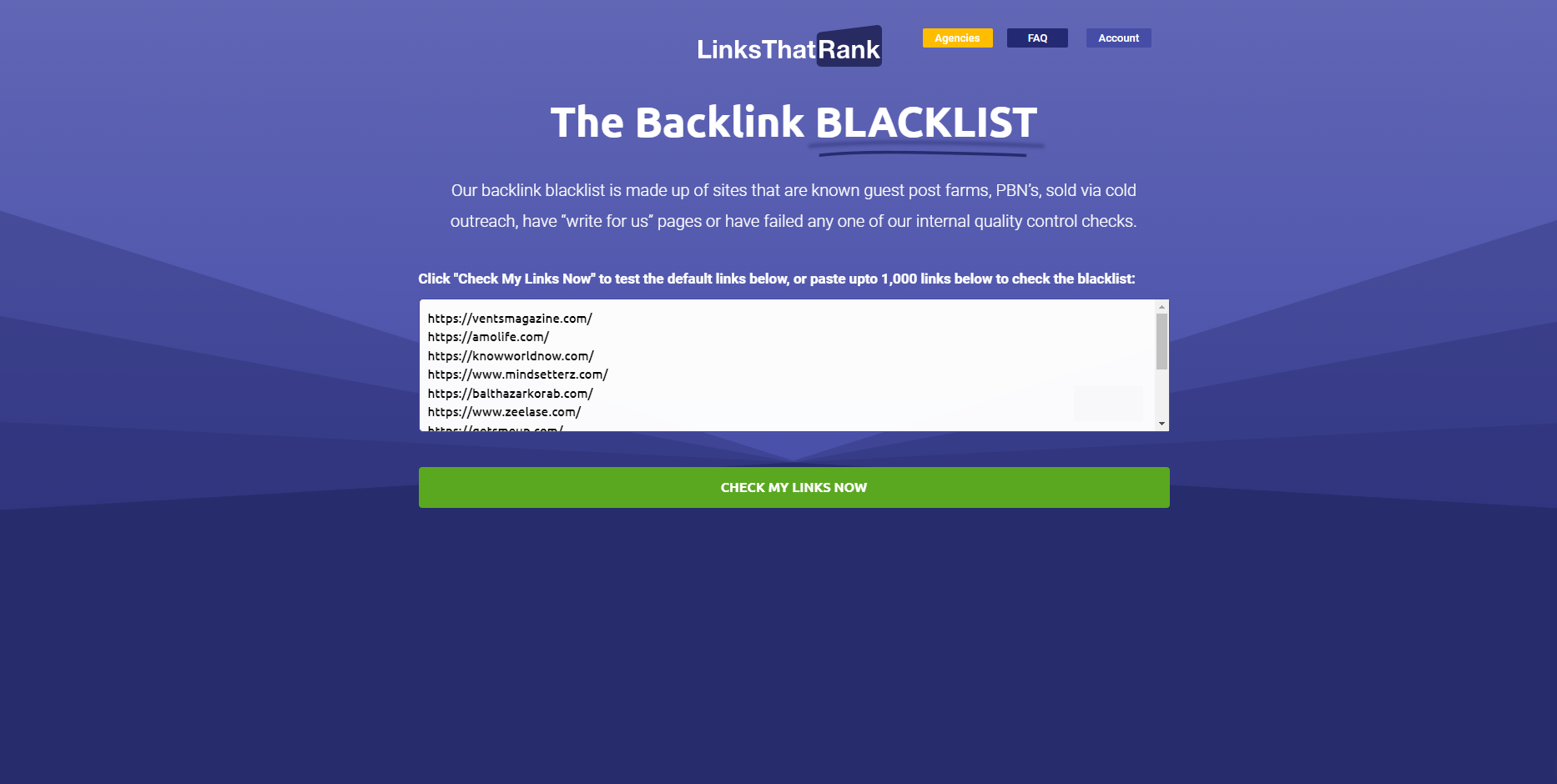
The free tool will tell you if the site is blacklisted.
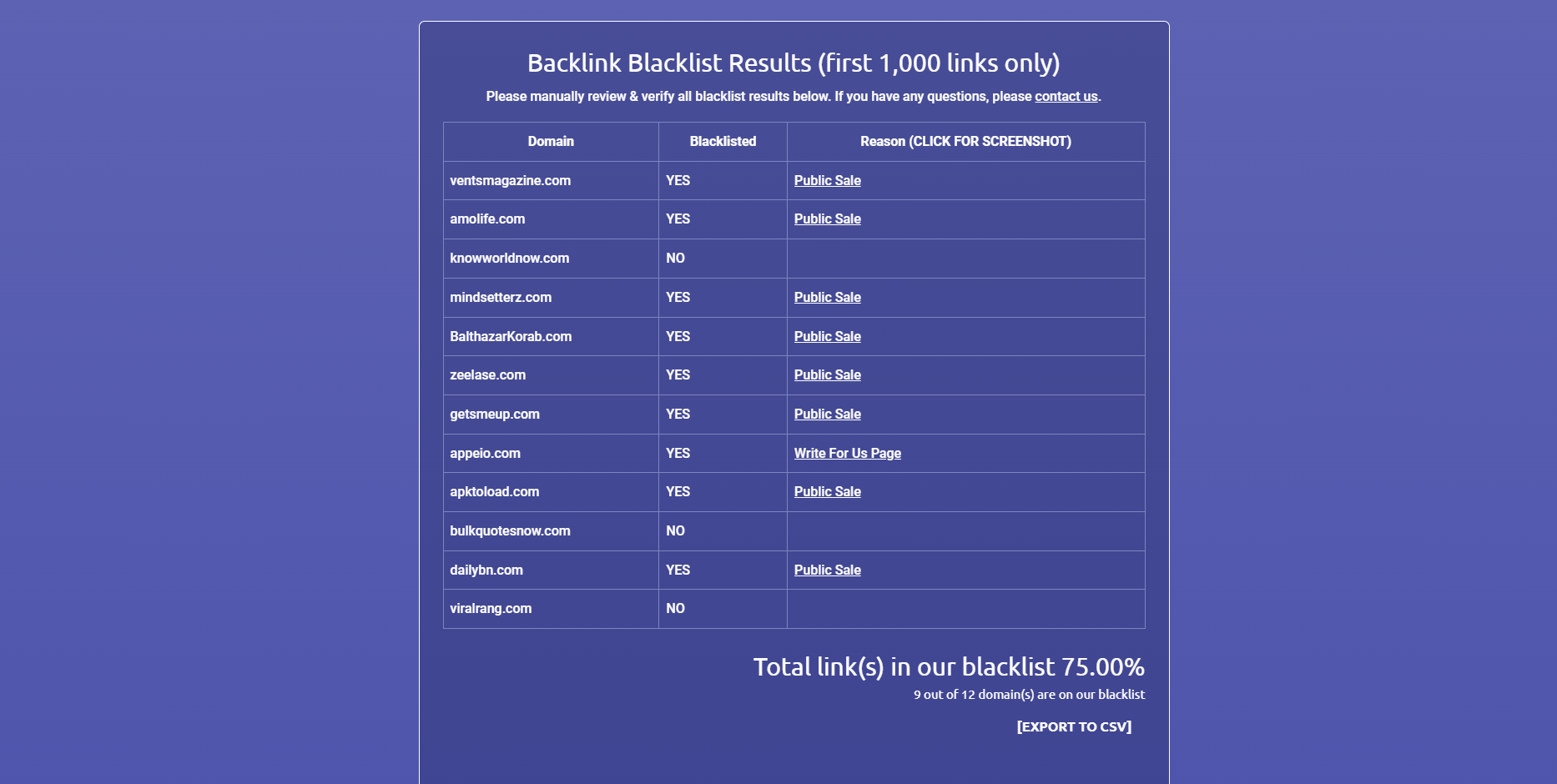
Each reason is linked to a screenshot that proves why the platform blacklisted the site.
It doesn’t show you other metrics to help you determine its quality. But as a free tool, the reason and screenshot of each domain are more than enough to prove that you have potentially bad links.
What to Do with Bad Links to Your Site
Spotting bad backlinks is the easy part. What you plan on doing with them is an executive decision that has no clear right or wrong answer.
For discussion, let’s say you discover that your site has toxic backlinks. There are two things you can do:
Do Nothing
Suppose the links haven’t negatively affected your site’s rankings. The best course of action is to stay put and observe.
Using your SEO tool of choice, you can check whether or not the toxic links affected your organic rankings from the day you acquired them.
It’s possible that your rankings could drop soon due to these links. But it’s also plausible that nothing will happen to your site’s SEO performance, given that Google is smart enough to disregard spammy and unnatural links built on your site.
But if nothing comes out of the toxic backlinks you found, don’t do anything about them.
It’s easy to be trigger-happy and do something about these links just to act on them. However, no action is something the only necessary action.
In this case, focus on the good parts of your websites and consider doubling down on them.
Continue executing the same tactics that have generated traffic to your site. Also, run tests to determine which techniques produce the best results in your campaign.
The point here is to constantly improve your site and not worry about something that hasn’t happened yet!
Disavow Them
If your website was fundamentally affected by bad backlinks, you have to disavow these links to recover the ground you lost on SERPs.
You will immediately know this upon receiving a warning on your Google Search Console regarding unnatural links.
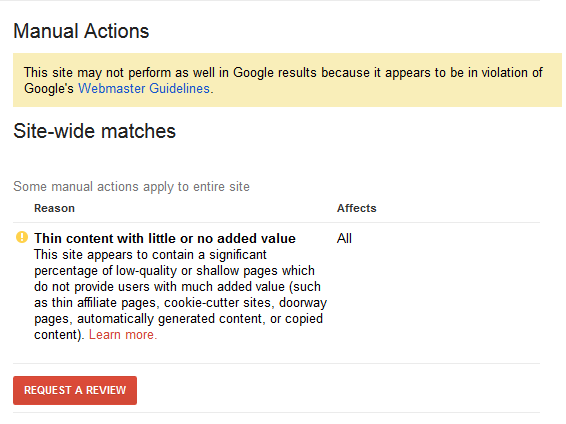
Google has documented the process of how you can adequately disavow your links. It also shows how you can undo previously disavowed links to your site.
To automatically create the disavow file to be uploaded on the Disavow links page on your Google Search Console, use a backlink tool like Monitor Backlinks to identify which links you plan on disavowing.
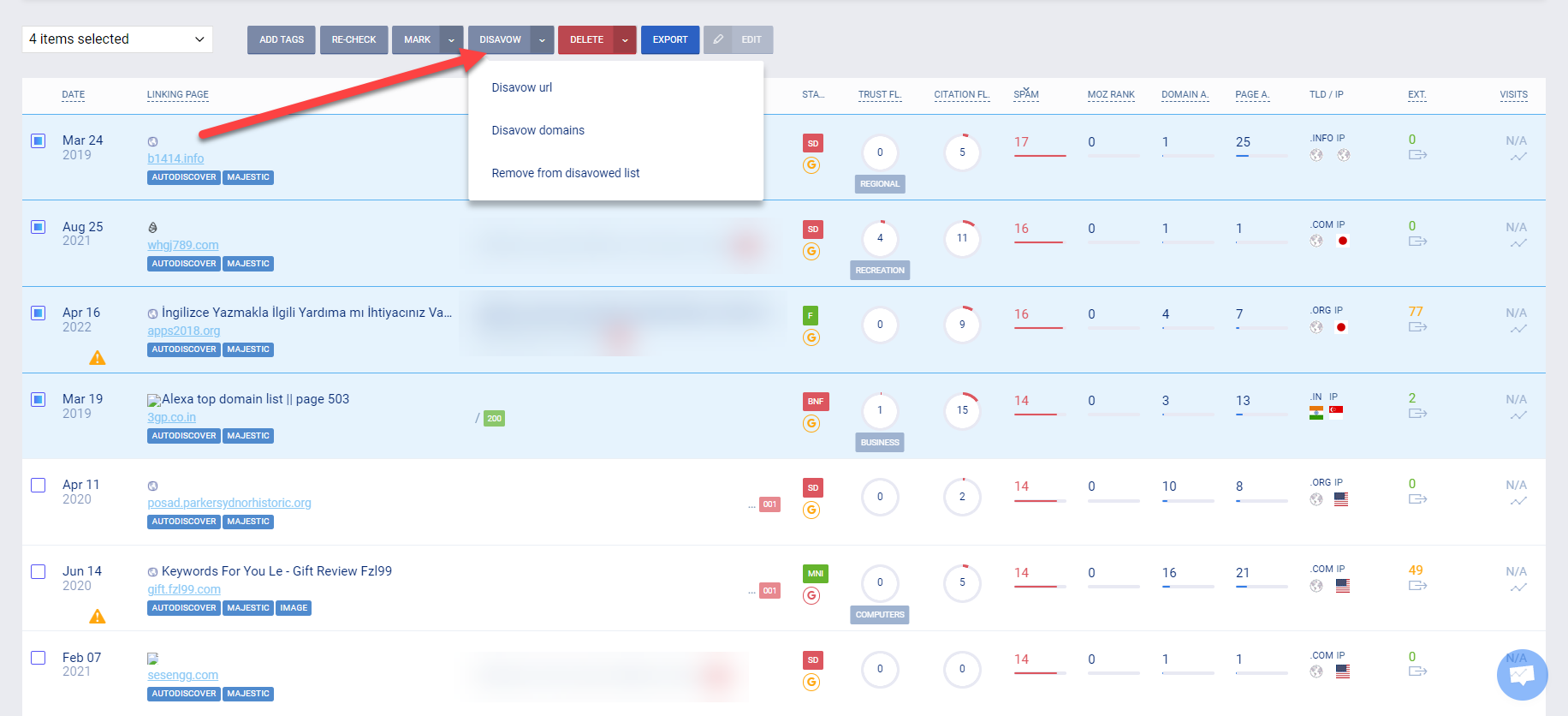
On its Disavow Tool, select which links to include in the file you must export from the tool and upload them on your Google Search Console.
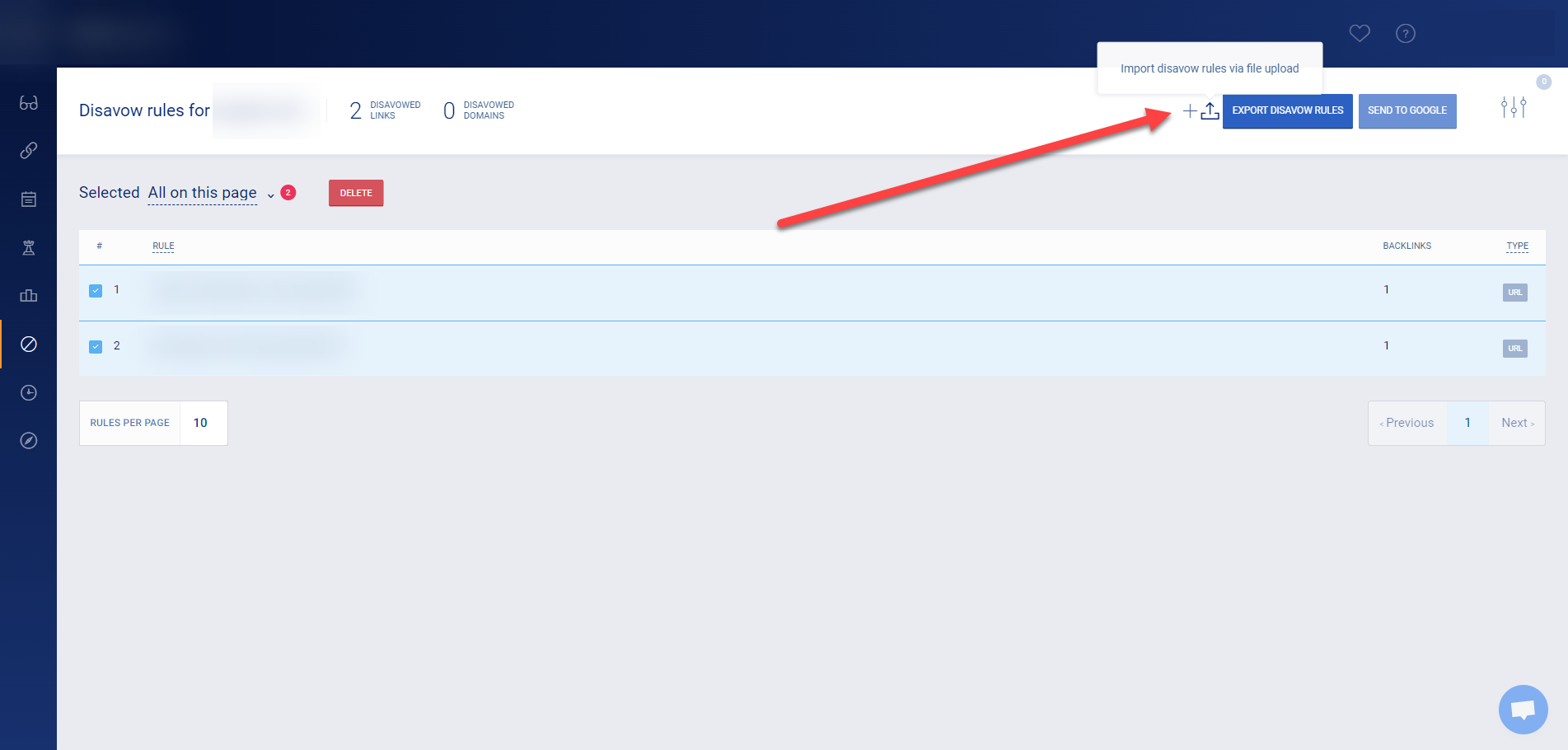
Again, unless Google issued a manual action against your site, it’s better not to disavow even the most toxic links on your site.
As mentioned, it’s unnecessary as the search engine can pick up which links to consider when ranking your site on SERPs.
Conclusion
There’s a lot to take in regarding spammy links.
Some of them were created because of a lack of due diligence while others are built by competitors envious of your site’s success.
At the same time, you don’t have to do anything with these backlinks unless it negatively impacts your search rankings. Only then should you consider disavowing spammy backlinks.
But if there’s anything to learn from this post, it’s that all sites have bad links one way or another.
What’s important is how you continue improving your SEO efforts with the information in this post.
Using the aforementioned tools above, you should be more diligent when it comes to monitoring your backlinks. They should also help you keep a close eye on whether the spammy links you receive will change your organic traffic for the worse.
Ultimately, knowing what are bad backlinks allows you to build better links that will help improve your search rankings.

Digital Nomad
I’m a full-blown Search Engine Optimization specialist earning the majority of my income from SEO-focused endeavours, including affiliate marketing, lead generation, as well as SEO services. Love travelling the world networking while working on my laptop. Life is a perception of your own reality. You have no excuses and should be making memories every single day.

0 Responses to Bad Links – Identifying Toxic Backlinks